使用Mix创建命令行工具
注意
网上的很多文档中的说明都使用了mix escriptize命令用于生成命令行工具, 在最新的Elixir版本中被改为mix escript.build, 请注意!
用Mix创建一个项目骨架
mix是一个Elixir自身支持的项目管理工具, 支持的功能有:
- 创建基本项目目录结构
- 管理依赖
- 编译
- 发布
下面我们使用mix来创建一个命令行工具的项目目录
mix new commandlinetools
cd commandlinetools
项目创建好以后, 编辑项目目录下的mix.exs项目描述文件, 在project函数内添加escript配置,并添加escript函数,如下:
def project do
[app: :commandlinetools,
version: "0.0.1",
elixir: "~> 1.0",
deps: deps,
escript: escript
]
end
def escript do
[main_module: Commandlinetools]
end
main_module 选项指定了命令行工具的入口模块, 该模块必须实现一个main/1函数, 打开lib/commandlinetools.ex, 实现main/1函数
defmodule Commandlinetools do
def main(args) do
IO.puts("命令行工具main函数实现")
end
end
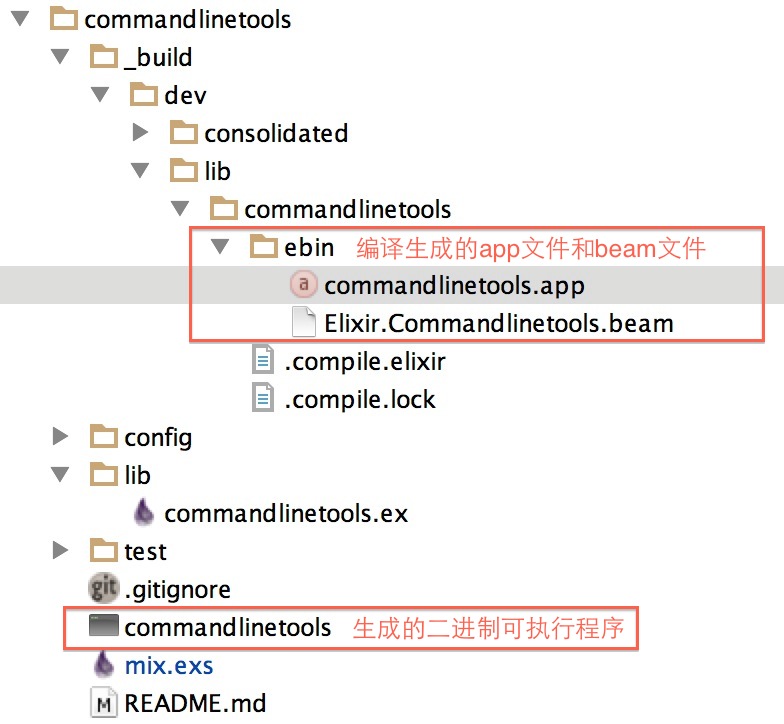
编译,生成可执行程序
root@0b85dcd174f2:~/ejabberd/elixir/commandlinetools# mix escript.build
lib/commandlinetools.ex:2: warning: variable args is unused
Compiled lib/commandlinetools.ex
Generated commandlinetools.app
Consolidated List.Chars
Consolidated Range.Iterator
Consolidated String.Chars
Consolidated Enumerable
Consolidated Access
Consolidated Inspect
Consolidated Collectable
Consolidated protocols written to _build/dev/consolidated
Generated escript commandlinetools with MIX_ENV=dev
运行
root@0b85dcd174f2:~/ejabberd/elixir/commandlinetools# ./commandlinetools
命令行工具main函数实现
解析命令行参数
命令行参数的解析, 我们需要用到OptionParser模块, 下面是增加了命令行选项解析的完整lib/commandlinetools.ex模块
defmodule Commandlinetools do
@moduledoc """
一个命令行模块, 作为一个示例讲解如何使用Mix工具开发一个二进制命令行工具
"""
def main(args) do
IO.puts("命令行工具main函数实现")
# 管道, args传递给parse_args函数, parse_args函数的返回值作为管道另一端process函数的第一个参数
args |> parse_args |> process
end
def parse_args(args) do
options = OptionParser.parse(args, switches: [help: :boolean], aliases: [h: :help])
# 输出解析后的选项
IO.puts("Options is #{inspect options}")
# 匹配
case options do
{ _, [ help: true], _} -> :help
{ _, [ vehicle ], _ } -> [vehicle, "eels"]
{ _, [ vehicle, fish ], _ } -> [vehicle, fish]
_ -> :help
end
end
@doc """
通过parse_args(args)的返回值匹配实际的process(args)命令处理函数
"""
def process([vehicle, fish]) do
IO.puts "My #{vehicle} is full of #{fish}."
end
@doc """
显示命令行帮助
"""
def process(:help) do
IO.puts """
Usage:
example [vehicle] [fish]
Options:
-h, [--help] # Show this help message and quit.
Description:
Excuse me, dear Sir, are there fish in your vehicle?
"""
System.halt(0)
end
end
重新编译命令行工具
root@0b85dcd174f2:~/ejabberd/elixir/commandlinetools# mix escript.build
Compiled lib/commandlinetools.ex
Generated commandlinetools.app
Consolidated List.Chars
Consolidated Range.Iterator
Consolidated String.Chars
Consolidated Enumerable
Consolidated Access
Consolidated Inspect
Consolidated Collectable
Consolidated protocols written to _build/dev/consolidated
Generated escript commandlinetools with MIX_ENV=dev
运行
root@0b85dcd174f2:~/ejabberd/elixir/commandlinetools# ./commandlinetools vehicle fish
命令行工具main函数实现
Options is {[], ["vehicle", "fish"], []}
My vehicle is full of fish.
参考资料
- Mix.Tasks.Escript.Build
http://elixir-lang.org/docs/stable/mix/Mix.Tasks.Escript.Build.html - How to create a command line utility with Elixir and mix
http://abstraction.killedthecat.net/create-command-line-utility-elixir-mix/ - Tutorial Create Command Line Tools With Elixir
https://github.com/rizafahmi/elixirdose-cli - 解析命令行参数
http://elixir-lang.org/docs/stable/elixir/OptionParser.html